Application of superabsorbent polymers in agriculture
javid keshtleyzeri Co.ltd
Today, protecting the environment and health of plants, animals and humans is considered as one of the main goals of countries. The use of absorbent polymers and hydrogel in agriculture has recently shown many advantages in soil improvement. These benefits include maintaining water content, reducing the consumption of soil nutrients, controlling the negative effects of water shortage and water stress in crops, and controlling some plant damage factors. Seed coating technology plays an important role in seed protection and facilitating plant growth. Absorbent polymers and hydrogels are used as seed coatings using growth regulators, pesticides, fertilizers and symbiotic materials. This article discusses the importance of different types of absorbent polymers and hydrogels in an integrated strategy to protect seeds, plants and soil in a balanced way.
Super absorbent polymers are used in agriculture as a new technology. These polymers have the ability to absorb and store water and are used in different sectors of agriculture. Some of the applications of superabsorbent polymers in agriculture are:
1. Improving soil hydration: By adding superabsorbent polymers to soil, soil hydration improves and soil moisture becomes more and more stable for plants.
2. Soil porosity control: Using super absorbent polymers, soil porosity is reduced and the water level in the soil is maintained.
3. Maintaining humidity in water sources: Using super absorbent plastics, the humidity of water sources such as rivers and lakes is maintained and water evaporation is reduced.
4. Reducing the need for irrigation: by using super absorbent polymers, the need for irrigation in dry and low water areas is reduced.
5. Preservation of fertilizer in the soil: The above-mentioned absorbent polymers have the ability to absorb and store fertilizer, so the fertilizers applied to the soil are better absorbed and prevent destruction by environmental factors.
6. Preservation of soil properties: By using super absorbent plastics, the physical and chemical properties of the soil are preserved and soil erosion is prevented.
7. Cultivation of gardens and greenhouses: Super absorbent plastics are used in gardens and greenhouses to maintain soil moisture and reduce the need for irrigation.
8. Enhancing seed germination: Super absorbent polymers can be used to improve seed germination by providing a consistent water supply to the seeds, promoting faster and healthier growth.
9. Drought resistance: Super absorbent polymers help plants withstand drought conditions by storing water in the soil and releasing it slowly to the roots, ensuring continuous hydration even during dry periods.
10. Nutrient retention: These polymers can also retain nutrients in the soil, preventing them from being washed away by rain or irrigation, and making them available for plant uptake over an extended period of time.
11. Erosion control: By improving soil structure and moisture retention, super absorbent polymers help prevent erosion caused by wind or water runoff, preserving the integrity of agricultural land.
12. Crop yield improvement: The use of super absorbent polymers in agriculture has been shown to increase crop yields by providing optimal moisture levels and nutrient availability to plants, resulting in healthier and more productive crops.
13. Environmental sustainability: By reducing water usage and preventing nutrient leaching, super absorbent polymers contribute to sustainable farming practices that conserve natural resources and minimize environmental impact.
14. Cost-effectiveness: Although initially more expensive than traditional irrigation methods, the long-term benefits of using super absorbent polymers in agriculture outweigh the costs by reducing water consumption, fertilizer usage, and crop losses due to drought or nutrient deficiencies.
Overall, the use of super absorbent polymers in agriculture offers numerous advantages for farmers, including improved soil hydration, reduced irrigation needs, enhanced crop growth, and environmental sustainability.
Super absorbent polymers
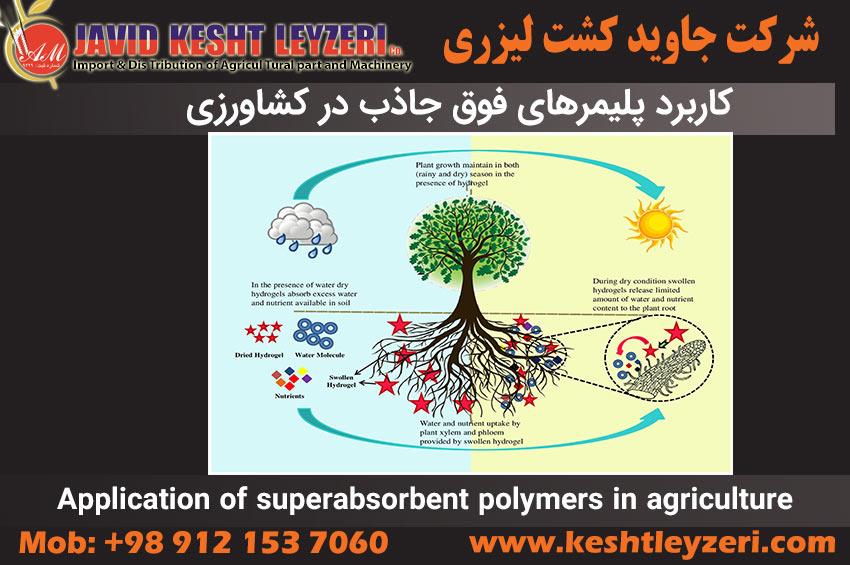
Absorbent polymers, which are also known as superabsorbent polymers, absorbent gels, abgel or hydrogel, are synthetic macromolecular materials that have osmotic properties and are able to accumulate water with a capacity higher than their volume up to 100 times. In addition, superabsorbent polymer is widely used in improving soil properties. These materials are generally composed of hydrophilic materials such as sugar and turn into a clear gel when in contact with water. Superabsorbent polymers are known as hydrophilic, three-dimensional and interconnected functional polymers and are able to increase the volume of water in the soil much higher than a hundred times their weight. Also, among other applications of these polymers, we can mention improving the performance of fertilizers and increasing the activity of soil microorganisms.
Challenges of using absorbent polymers
Superabsorbent polymer is a material used in agriculture and soil amendment. In addition to these useful applications, this polymer creates changes in the physical properties of the soil such as its porosity, density and structure. However, due to the reduced water consumption associated with the use of superabsorbent polymer, its performance may not be accurately determined. Also, there are some disadvantages for synthetic superabsorbent polymers. These polymers are not biodegradable and may even be toxic to the living environment. Research has shown that the super attractive polymer cannot be decomposed and if it is used excessively in agriculture or as a seed coating or soil amendment, it can have a great risk for plant health, soil fertility and even cause environmental pollution. It has been shown in several studies that the use of carbohydrate-based superabsorbent polymer is beneficial in the growth and germination of corn with less water consumption. Also, the use of superabsorbent polymer can increase plant survival in drought stress conditions. In another research, it has been shown that the use of 150 kg per hectare of ultra-attractive polymer and 1 liter per hectare of nitroxine leads to the highest yield of corn and its better growth.
Hydrogel
Hydrogel is a chain network of hydrophilic polymers that generally has many applications in the field of medicine. These materials are able to absorb body fluids and interact with the external environment. In addition, hydrogels can be used as drug carriers for wound healing.
The main application of hydrogels in agriculture is to reduce the need for irrigation. Hydrogels can be divided into two main groups from a physicochemical point of view. The properties of the first group of hydrogels are reversible and there are polymer chains with electrostatic forces and hydrogen bonds. This group is easily converted into polymer mixtures by heating, such as gelatin and agar. The second group are chemically stable hydrogels in which polymer chains are connected by stable covalent bonds and include starch and vinyl monomers such as acrylic acid, acrylamide, acrylonitil, and vinyl alcohol plasticization.
The use of hydrogels in agriculture, especially potassium or sodium polyacrylate hydrogels, has become very common for the following reasons. These hydrogels are easily decomposed in the soil and can be recycled, which makes them very suitable for agricultural use compared to other absorbent polymers. Moreover, hydrogels have shown remarkable and promising results as a soil amendment or for seed coating. Many researches have shown that the use of hydrogels as a soil conditioner may lead to improved water and fertilizer retention in the soil, improved soil aeration, reduced evaporation and transpiration, and enhanced seedling growth.
Application of hydrogel
In the field of agriculture, there are various conditions that may limit plant growth and reduce crop yield. For this reason, the use of hydrogels has been proposed as a suitable solution in dealing with these adverse environmental conditions. These hydrogels are used in various fields such as improving soil properties, water conservation, tolerance against drought stress and biotic and abiotic stresses, reducing the frequency of irrigation and saving water consumption, reducing the loss of seedlings and minimal use of fertilizers and pesticides in fields. are taken Although many researches have been conducted regarding the benefits of using hydrogel to cover rare seeds, there are also good studies in the field of using hydrogel to improve the water and fertilizer holding capacity in the soil, increase soil aeration and reduce evaporation and transpiration.
Biodegradation of hydrogels
In general, hydrogel polymers are very sensitive and can easily absorb into tissues and become implanted. But these hydrogels are easily destroyed when exposed to natural ultraviolet rays. Especially, polyacrylate is much more sensitive to soil aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms and easily decomposes into water, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. The decomposition of hydrogels may also have occurred through the activity of biologically decomposing fungi.
The importance of hydrogel in plant performance
A) The effect of hydrogel on seed germination: There is no definite effect of hydrogel on seed germination due to its treatment, but some studies have shown that this substance has a positive effect. For example, one study showed that the use of a superabsorbent hydrogel composition, which includes acrylamide and acrylic acid and was made using polyethylene glycol on starch, resulted in better germination of corn seeds and better seedling growth compared to Untreated seeds are hydrogelled.
b) The effect of hydrogel on plant growth: the use of hydrogel in the growth of different species has been effective in significantly increasing water mapping, especially in sandy soils. However, there are also reports that inappropriate use of hydrogel has resulted in plant mortality.
c) Prevention of drying: a number of studies have shown that the use of these materials in laboratory culture in order to increase the tolerance of rhizobia in water shortage conditions and prevent drying due to lack of moisture is a significant improvement. However, there are also conflicting reports.
seed coat
The seed coating method is one of the common methods to protect seeds against external factors such as salinity, lack of water, and possible pathogens. This method, by using foreign materials, helps seedlings to establish and germinate, and is especially effective in adverse conditions. The annual value of using this technology is one billion dollars. Also, seed coating is an economic solution for biological control of plant pathogens. With the dominance of living organisms, they have been encapsulated in different formulations, especially hydrogels. Also, this technology can play an effective role in germination with minimal water consumption. In any case, it should be noted that seed coating should not have a negative effect on the germination process and seed health and should not cause secondary seed dormancy.
Seed coating is the first line of defense against different climates and pathogens. Also, seed coat can regulate seed metabolism in response to adverse environmental conditions. This cover can be soft or hard. In the case of soft coating, it is dissolved and washed away by gradually moistening the surrounding of the seed and the seed is released. On the other hand, in the case of hard coat, after absorbing water, it will retain its shape and transfer moisture to the seed, and finally it will split and the seed will germinate.
Although in primary sources, seed coating is used only to change the shape and size of the seed, this coating can also include polymer technology for use in microbial inoculation, growth regulators, systemic treatment, pesticides, and the use of micro- and macro-fertilizers. Recent researches have shown that seed coating can effectively be used to transport food, biological control agents such as beneficial microorganisms and mycorrhizal fungi, improve plant growth and transport agrochemicals such as bactericide, fungicide and pesticide. The use of hydrogel in the formulation process of seed coating adds nutrients, microbes and biological toxins to the seed, and compared to the old methods, it has many advantages and has no negative impact on the surrounding environment. For example, the use of hydrogel in seed coating has improved seed aeration, significantly increased germination, and reduced drought stress symptoms in a species of the Fabiaceae family. In another study, it has been shown that the use of hydrogel as a seed coating in the early growth of corn kernels has caused a significant increase in seed germination and reduced drought stress symptoms in light drought stress conditions (irrigation of 77% of field capacity).
Corn seed polymer coating
Until now, the use of polymer coating for commercial corn seed has been less. Most of the commercial uses of polymer coating have been for the production of hybrid corn seeds. Because traditionally, the paternal line is planted a few days after the maternal line, these coatings are used for the paternal line seeds to synchronize flowering between the paternal and maternal lines. Over the past 20 years, more than 30 hybrid corn companies have used acrylic polymers to produce pedro seeds in fields. If these polymers are able to improve the plant population and the performance of corn seeds, there is a possibility of wide use of these polymers in the production of hybrid corn.
Conclusion
Currently, the use of innovative methods in plant protection in order to reduce dependence on chemical pesticides and preserve the environment has increased globally. The successful use of superabsorbent polymer and hydrogels in order to protect the soil and improve plant performance against adverse environmental conditions shows that these methods have a significant effect. Seed coating technology has also been considered as an interesting strategy to protect seeds against plant pathogens and improve its growth. In this article, how effective is the use of superabsorbent polymer and hydrogels. Superabsorbent polymer has many advantages, especially in improving and saving water and nutrients in soil. However, there are some disadvantages such as non-biodegradability and possible toxicity in superabsorbent polymers.For this reason, the use of suitable hydrogels, which have fewer advantages and disadvantages, bring promising results in seed and plant protection, and also ensure the maintenance of soil fertility, reduction of water consumption, and reduction of nutrient loss.






